If a project's net present value (NPV) is zero, then its internal rate of return (IRR) will be:
Question 48 IRR, NPV, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds, market efficiency
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A three year project's NPV is negative. The cash flows of the project include a negative cash flow at the very start and positive cash flows over its short life. The required return of the project is 10% pa. Select the most correct statement.
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the project detailed in the table below?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. All answers are given as effective annual rates.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
A project has an internal rate of return (IRR) which is greater than its required return. Select the most correct statement.
A project's net present value (NPV) is negative. Select the most correct statement.
A project's NPV is positive. Select the most correct statement:
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 |
The required return on the project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of this project? The following choices are effective annual rates. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
A project's Profitability Index (PI) is less than 1. Select the most correct statement:
Question 218 NPV, IRR, profitability index, average accounting return
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A firm is considering a business project which costs $11m now and is expected to pay a constant $1m at the end of every year forever.
Assume that the initial $11m cost is funded using the firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
A firm is considering a business project which costs $10m now and is expected to pay a single cash flow of $12.1m in two years.
Assume that the initial $10m cost is funded using the firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.
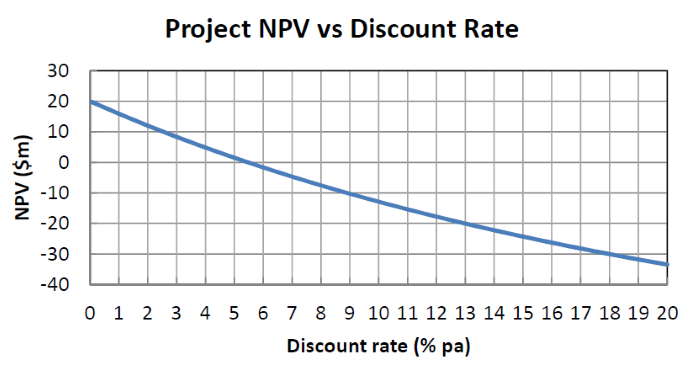
For what discount rate or range of discount rates would you accept and commence the project?
All answer choices are given as approximations from reading off the graph.
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.

Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
An investor owns an empty block of land that has local government approval to be developed into a petrol station, car wash or car park. The council will only allow a single development so the projects are mutually exclusive.
All of the development projects have the same risk and the required return of each is 10% pa. Each project has an immediate cost and once construction is finished in one year the land and development will be sold. The table below shows the estimated costs payable now, expected sale prices in one year and the internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cost now ($) |
Sale price in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Petrol station | 9,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 22.22 |
| Car wash | 800,000 | 1,100,000 | 37.50 |
| Car park | 70,000 | 110,000 | 57.14 |
Which project should the investor accept?
An investor owns a whole level of an old office building which is currently worth $1 million. There are three mutually exclusive projects that can be started by the investor. The office building level can be:
- Rented out to a tenant for one year at $0.1m paid immediately, and then sold for $0.99m in one year.
- Refurbished into more modern commercial office rooms at a cost of $1m now, and then sold for $2.4m when the refurbishment is finished in one year.
- Converted into residential apartments at a cost of $2m now, and then sold for $3.4m when the conversion is finished in one year.
All of the development projects have the same risk so the required return of each is 10% pa. The table below shows the estimated cash flows and internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cash flow now ($) |
Cash flow in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Rent then sell as is | -900,000 | 990,000 | 10 |
| Refurbishment into modern offices | -2,000,000 | 2,400,000 | 20 |
| Conversion into residential apartments | -3,000,000 | 3,400,000 | 13.33 |
Which project should the investor accept?
Question 542 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to double every 10 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 543 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to triple every 5 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
You're considering a business project which costs $11m now and is expected to pay a single cash flow of $11m in one year. So you pay $11m now, then one year later you receive $11m.
Assume that the initial $11m cost is funded using the your firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about the net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
Question 915 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For a share price to double over 7 years, what must its capital return be as an effective annual rate?
You work for XYZ company and you’ve been asked to evaluate a new project which has double the systematic risk of the company’s other projects.
You use the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) formula and input the treasury yield (rf), market risk premium (rm−rf) and the company’s asset beta risk factor (βXYZ) into the CAPM formula which outputs a return.
This return that you’ve just found is:
Your 18 year old friend is considering what to do with their working life until they retire at age 65. They've sought your advice.
For simplicity, ignore taxes and assume that wages will be paid annually in arrears and will be constant (zero growth). The abbreviation 'k' (Greek kilo) means thousands, so 1k is 1000.
Let the present be time zero (t=0) and the year that you retire be time 47 (t=47).
Your friend is deciding between working as a:
- Builder's apprentice for 2 years earning $20k pa (2 payments from t=1 to t=2 inclusive), then beginning work as a builder for $90k pa (45 annual payments from t=3 to 47 inclusive);
- Retail shop salesperson for $50k pa (47 payments from t=1 to t=47 inclusive).
You estimate that the required return is 5% pa with either career, and that they're equally risky. The cashflows are shown below:
| Career Choices and Cash Flows | ||
| Time | Builder | Retailer |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 20 | 50 |
| 2 | 20 | 50 |
| 3 | 90 | 50 |
| 4 | 90 | 50 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 47 | 90 | 50 |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Comparing the two alternatives, being a builder compared to a retail salesperson, the:
Your 18 year old friend is considering what to do with their working life until they retire at age 65. They've sought your advice.
For simplicity, ignore taxes and assume that wages will be paid annually in arrears and will be constant (zero growth). The abbreviation 'k' (Greek kilo) means thousands, so 1k is 1000.
Let the present be time zero (t=0) and the year of retirement is time 47 (t=47).
Your friend is deciding between:
- Studying at university for 3 years, costing $30k at the start of each year (3 cash outflows at t=0, 1 & 2), then beginning work as a financial planner for $100k pa (44 annual payments from t=4 to 47 inclusive);
- Working as a builder's apprentice for 2 years, earning $20k pa (2 cash inflows at t=1 and t=2), then beginning work as a builder for $90k pa (45 annual payments from t=3 to 47 inclusive);
You estimate that the required return is 5% pa with either career, and that they're equally risky. The cashflows are shown below:
| Career Choices and Cash Flows | ||
| Time | Planner | Builder |
| 0 | -30 | 0 |
| 1 | -30 | 20 |
| 2 | -30 | 20 |
| 3 | 0 | 90 |
| 4 | 100 | 90 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 47 | 100 | 90 |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Comparing the two alternatives, being a financial planner compared to a builder, the:
Find the internal rate of return (IRR) of buying a $100 stock now that's expected to pay annual dividends forever, with the next $8 dividend to be paid in one year (t=1). The dividend is expected to grow forever at 3% per annum . Therefore the second dividend (paid at t=2) is expected to be $8.24 (=8*(1+0.03)^1). The IRR of buying this stock now is:
Find the market-implied total required return on equity of buying a $10 stock now that's expected to pay annual dividends forever, with the next $0.50 dividend to be paid in one year (t=1). The dividend is expected to grow forever at 2% per annum. Therefore the second dividend (paid at t=2) is expected to be $0.51 (=0.5*(1+0.02)^1). Assume that the stock can be accurately valued with the DDM. The stock's market-implied total required return on equity is:
Question 1091 NPV, perpetuity with growth, IRR, mutually exclusive projects, real estate
An investor owns an empty block of land that was bought for $3 million a few years ago, but could be sold at auction for $2 million now. The land has local government approval to be developed into either:
- Low-rise townhouses costing $11 million now (t=0) that can be rented for $2 million in the first year, paid at the end of that year (t=1), and then rent is expected to grow by 4% pa every year forever; or
- High rise apartments costing $90 million now (t=0) that can be rented for $14 million in the first year, paid at the end of that year (t=1), and then rent is expected to grow by 1% pa every year forever.
The government will only allow a single development so the projects are mutually exclusive.
These projects have the same risk and 9% pa required return. Both will be fully constructed in one year, at which point tenants will move in and pay rent annually in advance, with the growth rates given. Ignore all maintenance costs, tenant vacancies, taxes and so on. All answer options are rounded to 6 decimal places. Compare the two projects against selling the land. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Your boss the chief financial officer (CFO) asked you to complete the analysis of 3 different projects under consideration by the company's board. All projects require an initial investment and then provide a perpetuity of cash flows with zero growth. All are equally risky with the same 10% pa required return. All figures are rounded to 4 decimal places. The projects can all be accepted and funded, they're not mutually exclusive.
The projects' initial costs and perpetual annual cash flows were provided by the engineering and marketing departments, and the CFO completed some of the NPV's and IRR's but ran out of time and gave it to you to finish. This data is believed to be accurate. You calculated the remaining NPV's and IRR's in bold, and made some conclusions about which projects to accept or reject (stated in answer option d). The CFO thanked you for your swift work, but said there's just one thing wrong with your calculations or conclusions, and asked you to fix it up before the table and conclusions are shown at the board meeting tomorrow.
| Projects with 10% pa required return | ||||
| Initial cash flow at t=0 |
Perpetual annual cash flow from t=1 |
NPV | IRR | |
| ($m) | ($m) | ($m) | (% pa) | |
| Project A | -160 | 19 | 30 | (a) 11.875 |
| Project B | -2,200 | 190 | (b) -300 | 8.6364 |
| Project C | -20,000 | 1,600 | (c) -4,000 | 8 |
Which one of the following calculations or conclusions is NOT correct?
A house worth $700k is expected to earn $30k pa gross rent revenue and incur rental costs of $10k pa over the next year. Note that the units 'k' (Greek kilo) represent thousands. Assume that these cash flows are expected one year from now, so they’re received and paid annually in arrears.
If the gross rent revenue and costs increase by 2% per annum and houses can be valued as a perpetuity, what is the internal rate of return (IRR) of buying this house asset? Ignore taxes.